Auf dieser Seite finden Sie eine Sammlung von Links zu wissenschaftlichen Veröffentlichungen, die für dieses Projekt relevant sind oder die dazu beitragen können, ein tieferes exemplarisches Verständnis über die Prozesse und Umstände zu erlangen, welche möglicherweise in einem Zusammenhang mit der hier vorgestellten Neuinterpretation der Germania Magna stehen. Dabei handelt es sich um Veröffentlichungen unterschiedlicher Forschungsbereiche.
Die Sammlung umfasst:
- Primärliteratur: Wissenschaftliche Veröffentlichungen, die die Ergebnisse neuer Forschung präsentieren.
- Sekundärliteratur: Wissenschaftliche Veröffentlichungen, die die Primärliteratur zusammenfassen, analysieren oder interpretieren.
- Vergleichende Literatur: Veröffentlichungen, die Ihnen exemplarisch ähnliche Prozesse und Umstände in anderen Kontexten aufzeigen.
- Weitere Ressourcen: Links zu Websites, Datenbanken und anderen Ressourcen, die für die Neuinterpretation relevant sein können.
Die folgenden Publikationen sollen dabei helfen, bestimmte Fragestellungen exemplarisch zu beantworten, welche in einem möglichen Zusammenhang mit den notwendigen Prozessen und Vorgängen stehen, die für eine umfangreiche Landschaftstransformation erforderlich sind. Hierzu zählen beispielsweise Überlegungen über tektonische Bruchereignisse und Rift-Systeme, mit entsprechender Auswirkung auf maritime Rutschungsereignisse und die Entstehung neuer Sedimentationsbecken.
- DIE ENTSTEHUNG DES VULKANISCHEN KAOLINS UND DAS ANDESIT-PROBLEMDie Kaoline werden in Literatur meist als Verwitterungsprodukte feldspatreicher, saurer Gesteine betrachtet. Die im Zuge der schnellen Aufwärtsentwicklung der keramischen Industrie vorangetriebenen Arbeiten über die Kaolin-Geologie zeigten es, dass die türkischen Kaoline hauptsächlich an die vulkanischen Gesteine gebunden sind. Für die Bildung der Kaolinlagerstätten ist es notwendig, dass die Kaolinisierung der … WeiterlesenDIE ENTSTEHUNG DES VULKANISCHEN KAOLINS UND DAS ANDESIT-PROBLEM
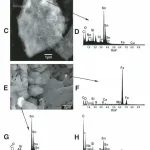
- Foraminifera in the glacial erratic rock Sternberger Gestein from northern GermanyDOI http://dx.doi.org/10.61551/gsjfr.54.3.249 Abstract This study is part of a project that aims to provide the first comprehensive analysis of foraminifera in glacial erratics. Such studies may be used to clarify the origin of glacial erratics and serve as indicators of the direction of glacial movements. The glacial erratics, which were deposited … WeiterlesenForaminifera in the glacial erratic rock Sternberger Gestein from northern Germany
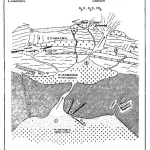
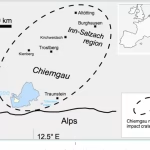
- The Chiemgau Meteorite Impact Strewn Field and the Digital Terrain Model: “Earthquake” Liquefaction from Above and from BelowDOI http://dx.doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.11274.79041 Abstract The Chiemgau strewn field discovered and established in the early new millennium(Schryvers and Raeymaekers, 2004; Schüssler et al., 2005; Rösler et al. 2005, Rappenglück,M. et al., 2005, Hoffmann et al., 2005, 2006; Yang et al 2008), extensively investigated in thefollowing decade until today (Ernstson et al. 2010, 2011, … WeiterlesenThe Chiemgau Meteorite Impact Strewn Field and the Digital Terrain Model: “Earthquake” Liquefaction from Above and from Below
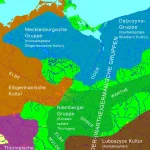
- Neues zur „Odergermanischen Gruppe“: Das innere Barbaricum an der unteren Oder im 5.–6. Jh. ADDOI https://doi.org/10.11588/heidok.00015918 Abstract In the early Migration Period (Period D), the climate worsened dramatically and weather became very cool and dry in the course of only a few decades. Very poor conditions for land cultivation and animal husbandry resulted from this, which withdrew their livelihood in many places from the Germanic … WeiterlesenNeues zur „Odergermanischen Gruppe“: Das innere Barbaricum an der unteren Oder im 5.–6. Jh. AD
- Herrschaftswechsel als Zäsur? Thüringen im Frankenreich – eine andere GeschichteDOI https://doi.org/10.1515/9783111128818-014 Abstract Der Band analysiert in enger interdisziplinärer Debatte von Archäologen und Historikern die Dukate des Merowingerreiches einschließlich ihrer möglichen spätantiken Vorläufer. Ziel ist ein systematischer Vergleich von duces und Dukaten innerhalb des Frankenreiches des 6. bis 8. Jahrhunderts sowie weiterer ausgewählter Beispiele. Dabei wird jeweils nach Zeitpunkt, Voraussetzungen und Umständen ihrer … WeiterlesenHerrschaftswechsel als Zäsur? Thüringen im Frankenreich – eine andere Geschichte
- Vulkanismus in Mitteldeutschland. Band 2: Explosiver Vulkanismus im Bereich der Halle-Störung zwischen Halle (Saale) und Leipzig. Die Tiefbohrung Lochau 7/65.Beschreibung Bei dieser Buchreihe handelt es sich um eine Collage anwendungsorientierter Arbeiten aus den Jahren 2002 – 2020, die mit Bezug zu Vulkanismus in Sachsen-Anhalt und Sachsen ausgeführt wurden. Die Arbeiten umfassen ingenieurgeologische, geotechnische und wissenschaftliche Aspekte. Beleuchtet werden vor allem verschiedene Aufschlüsse und Bohrungen an unterschiedlichen Standorten Es sind in … WeiterlesenVulkanismus in Mitteldeutschland. Band 2: Explosiver Vulkanismus im Bereich der Halle-Störung zwischen Halle (Saale) und Leipzig. Die Tiefbohrung Lochau 7/65.
- Vulkanismus in Mitteldeutschland. Band 4: Explosiver Vulkanismus im Bereich der Halle-Störung. Die Campusbohrung 3 in Heide SüdBeschreibung Bei dieser Buchreihe handelt es sich um eine Collage anwendungsorientierter Arbeiten aus den Jahren 2002 – 2020, die mit Bezug zu Vulkanismus in Sachsen-Anhalt und Sachsen ausgeführt wurden. Die Arbeiten umfassen ingenieurgeologische, geotechnische und wissenschaftliche Aspekte. Beleuchtet werden vor allem verschiedene Aufschlüsse und Bohrungen an unterschiedlichen Standorten Es sind in … WeiterlesenVulkanismus in Mitteldeutschland. Band 4: Explosiver Vulkanismus im Bereich der Halle-Störung. Die Campusbohrung 3 in Heide Süd
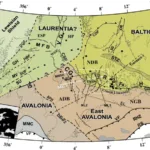
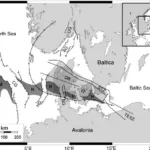
- A new tectonic model for the Laurentia-Avalonia-Baltica sutures in the North Sea: A case study along MONA LISA profile 3DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2006.09.017 Abstract We present a new model for the lithospheric structure of the transitions between Laurentia, Avalonia and Baltica in the North Sea, northwestern Europe based on 2¾D potential field modelling of MONA LISA profile 3 across the Central Graben, with constraints from seismic P-wave velocity models and the crustal … WeiterlesenA new tectonic model for the Laurentia-Avalonia-Baltica sutures in the North Sea: A case study along MONA LISA profile 3
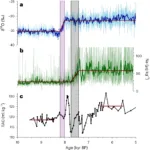
- What caused terrestrial dust loading and climate downturns between A.D. 533 and 540?DOI https://doi.org/10.1130/2014.2505(23) Abstract Sn-rich particles, Ni-rich particles, and cosmic spherules are found together at four discrete stratigraphic levels within the 362–360 m depth interval of the Greenland Ice Sheet Project 2 (GISP2) ice core (72.6°N, 38.5°W, elevation: 3203 m). Using a previously derived calendar-year time scale, these particles span a time … WeiterlesenWhat caused terrestrial dust loading and climate downturns between A.D. 533 and 540?
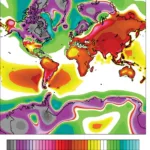
- Continental-scale temperature variability during the past two millenniaDOI https://doi.org/10.1038/ngeo1797 Abstract Past global climate changes had strong regional expression. To elucidate their spatio-temporal pattern, we reconstructed past temperatures for seven continental-scale regions during the past one to two millennia. The most coherent feature in nearly all of the regional temperature reconstructions is a long-term cooling trend, which ended late … WeiterlesenContinental-scale temperature variability during the past two millennia
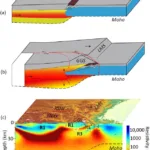
- Seismic velocity structure of crustal intrusions in the Danish BasinDOI https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2011.11.019 We image the east- and westward extent of a crustal high-velocity body, the thickness of a layered sequence around the Moho at the flank of the body, and the uppermost mantle velocity along the 320 km long refraction and wide-angle reflection seismic profile ESTRID 2007 in the Danish Basin. … WeiterlesenSeismic velocity structure of crustal intrusions in the Danish Basin
- Mechanism for the Uplift of Gongga Shan in the Southeastern Tibetan Plateau Constrained by 3D Magnetotelluric DataDOI http://dx.doi.org/10.1029/2021GL097394 Abstract Plain Language Summary Continent‐continent collisions are an important tectonic process and have controlled the formation of the modern continents. The India‐Asia collision is the best modern example and has produced both a high elevation plateau and the world’s highest mountain belts. A range of tectonic processes occurs during … WeiterlesenMechanism for the Uplift of Gongga Shan in the Southeastern Tibetan Plateau Constrained by 3D Magnetotelluric Data
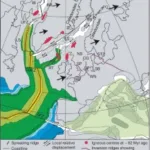
- Dynamics of Mid-Palaeocene North Atlantic rifting linked with European intra-plate deformationsDOI https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06379 Abstract The process of continental break-up provides a large-scale experiment that can be used to test causal relations between plate tectonics and the dynamics of the Earth’s deep mantle1,2. Detailed diagnostic information on the timing and dynamics of such events, which are not resolved by plate kinematic reconstructions, can … WeiterlesenDynamics of Mid-Palaeocene North Atlantic rifting linked with European intra-plate deformations
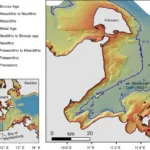
- A submerged Stone Age hunting architecture from the Western Baltic SeaDOI https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2312008121 Abstract The Baltic Sea basins, some of which only submerged in the mid-Holocene, preserve Stone Age structures that did not survive on land. Yet, the discovery of these features is challenging and requires cross-disciplinary approaches between archeology and marine geosciences. Here, we combine shipborne and autonomousunderwater vehicle hydroacoustic data … WeiterlesenA submerged Stone Age hunting architecture from the Western Baltic Sea
- Sea-level change, glacial rebound and mantle viscosity for northern EuropeKurt Lambeck, Catherine Smither, Paul Johnston, Sea-level change, glacial rebound and mantle viscosity for northern Europe, Geophysical Journal International, Volume 134, Issue 1, July 1998, Pages 102–144
- Continuous record of Holocene sea-level changes and coastal development of the Kattegat island Læsø (4900 years BP to present)DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.37570/bgsd-2016-64-01 Læsø is the largest island of the Kattegat–Skagerrak region and exposes a vast array of relative sealevel (RSL) indicators, mainly raised beach ridges, swales, lagoons and saltmarshes. The physical environment of continuous glacial rebound, excessive supply of sediment, shallow surrounding waters, low amplitudes of near-shore waves, and micro-tidal conditions … WeiterlesenContinuous record of Holocene sea-level changes and coastal development of the Kattegat island Læsø (4900 years BP to present)
- Holocene Relative Sea-Level Changes from Near-, Intermediate-, and Far-Field LocationsDOI https://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s40641-015-0029-z Abstract Holocene relative sea-level (RSL) records exhibit spatial and temporal variability that arises mainly from the interaction of eustatic (land ice volume and thermal expansion) and isostatic (glacio- and hydro-) factors. We fit RSL histories from near-, intermediate-, and far-field locations with noisy-input Gaussian process models to assess rates … WeiterlesenHolocene Relative Sea-Level Changes from Near-, Intermediate-, and Far-Field Locations
- Abrupt Holocene ice loss due to thinning and ungrounding in the Weddell Sea EmbaymentDOI https://doi.org/10.1038/s41561-024-01375-8 Abstract The extent of grounded ice and buttressing by the Ronne Ice Shelf, which provides resistance to the outflow of ice streams, moderate West Antarctic Ice Sheet stability. During the Last Glacial Maximum, the ice sheet advanced and was grounded near the Weddell Sea continental shelf break. The timing … WeiterlesenAbrupt Holocene ice loss due to thinning and ungrounding in the Weddell Sea Embayment
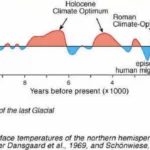
- One Thousand Centuries of Climatic Record from Camp Century on the Greenland Ice SheetDOI http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.166.3903.377 Abstract A correlation of time with depth has been evaluated for the Camp Century, Greenland, 1390 meter deep ice core. Oxygen isotopes in approximately 1600 samples throughout the core have been analyzed. Long-term variations in the isotopic composition of the ice reflect the climatic changes during the past nearly … WeiterlesenOne Thousand Centuries of Climatic Record from Camp Century on the Greenland Ice Sheet
- The catastrophic final flooding of Doggerland by the Storegga Slide tsunamiDOI https://doi.org/10.4312/dp.35.1 Abstract Around 8200 calBP, large parts of the now submerged North Sea continental shelf (‘Doggerland’) were catastrophically flooded by the Storegga Slide tsunami, one of the largest tsunamis known for the Holocene, which was generated on the Norwegian coastal margin by a submarine landslide. In the present paper, we … WeiterlesenThe catastrophic final flooding of Doggerland by the Storegga Slide tsunami
- Rapid Quaternary subsidence in the northwestern German North SeaDOI https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-29638-6 Abstract 3D and 2D seismic data reveal the base-reflection of the Quaternary in the northwestern German North Sea locally at depths of more than 1000 m. This indicates extremely fast subsidence, with a rate of up to 480 m/Ma during the Quaternary, resulting in a NNW-SSE oriented sedimentary depocentre. Distinct iceberg … WeiterlesenRapid Quaternary subsidence in the northwestern German North Sea
- The Thor suture zone: From subduction to intraplate basin settingDOI http://dx.doi.org/10.1130/G37958.1 Abstract The crustal seismic velocity structure of northwestern Europe shows a low P-wave velocity zone (LVZ) in the lower crust along the Caledonian Thor suture zone (TSZ) that cannot be easily attributed to Avalonia or Baltica plates abutting the TSZ. The LVZ appears to correspond to a hitherto unrecognized … WeiterlesenThe Thor suture zone: From subduction to intraplate basin setting
- Fault system evolution in the Baltic Sea area west of Rügen, NE GermanyDOI https://doi.org/10.1144/sp469.24 Abstract Based on reprocessed offshore seismic lines acquired during oil and gas exploration in the 1980s, we reconstruct the formation and reactivation of major fault systems in the southern Baltic Sea area since the late Paleozoic. The geological evolution of different crustal blocks from the Caledonian Avalonia-Baltica collision until … WeiterlesenFault system evolution in the Baltic Sea area west of Rügen, NE Germany
- Germania magna – Ein neuer Blick auf eine alte Karte. Entzerrte geographische Daten des Ptolemaios für die antiken Orte zwischen Rhein und Weichsel.DOI https://doi.org/10.11588/ger.2011.96480 Abstract This paper deals with the geographical indications for Germania magna in the Geographike Hyphegisis (ca. AD 150) of Claudius Ptolemaeus. Previous attempts at the identification of Ptolemaic locations were neither comprehensive nor based on a qualified analysis of the ancient data. By means of the geodetic-statistical analytic method … WeiterlesenGermania magna – Ein neuer Blick auf eine alte Karte. Entzerrte geographische Daten des Ptolemaios für die antiken Orte zwischen Rhein und Weichsel.