Mechanism for the Uplift of Gongga Shan in the Southeastern Tibetan Plateau Constrained by 3D Magnetotelluric Data
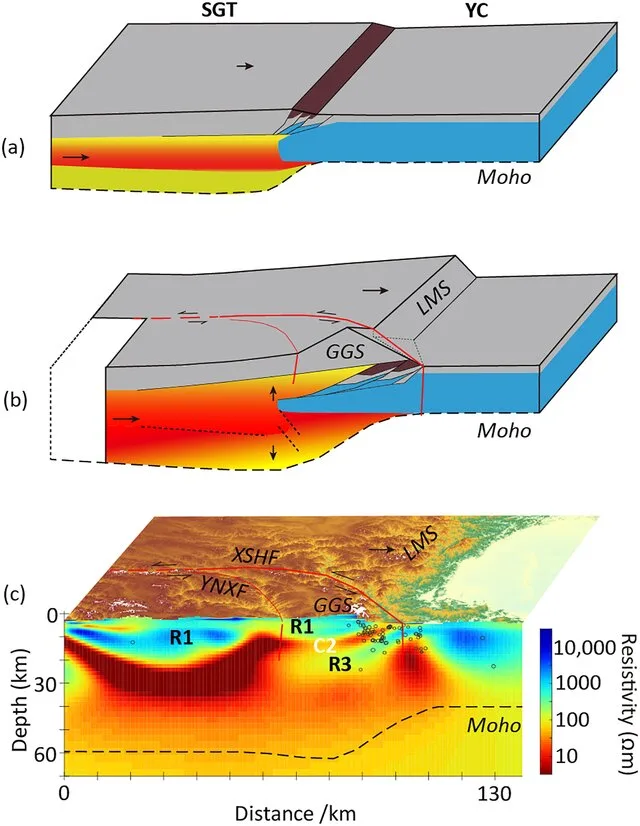
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.1029/2021GL097394 Abstract Plain Language Summary Continent‐continent collisions are an important tectonic process and have controlled the formation of the modern continents. The India‐Asia collision is the best modern example and has produced both a high elevation plateau and the world’s highest mountain belts. A range of tectonic processes occurs during these collisions as the crust deforms including extrusion and perhaps crustal flow. Within these collision zones, there are locations of especially rapid uplift that have not been explained with existing geodynamic models. This paper investigates this process through a study of Gongga Shan—a mountain on the eastern edge of the Tibetan Plateau, where uplift continues at a rate of 2–3 mm per year and has formed peaks greater than 7,500 m in elevation. 3D inversion of an array of magnetotelluric data has produced a well‐constrained crustal resistivity model for the GGS area. It reveals that the GGS crust is … Read moreMechanism for the Uplift of Gongga Shan in the Southeastern Tibetan Plateau Constrained by 3D Magnetotelluric Data