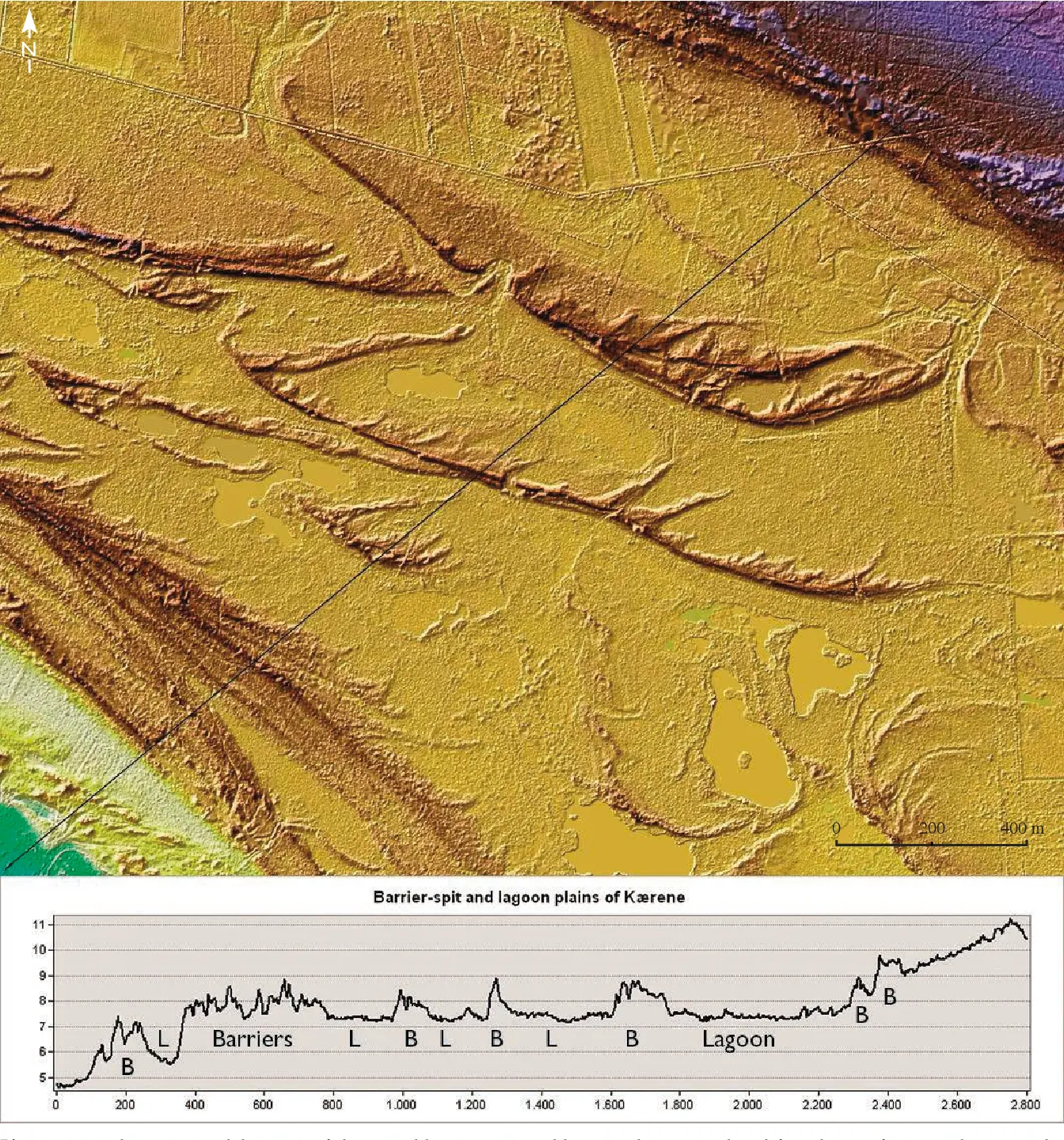
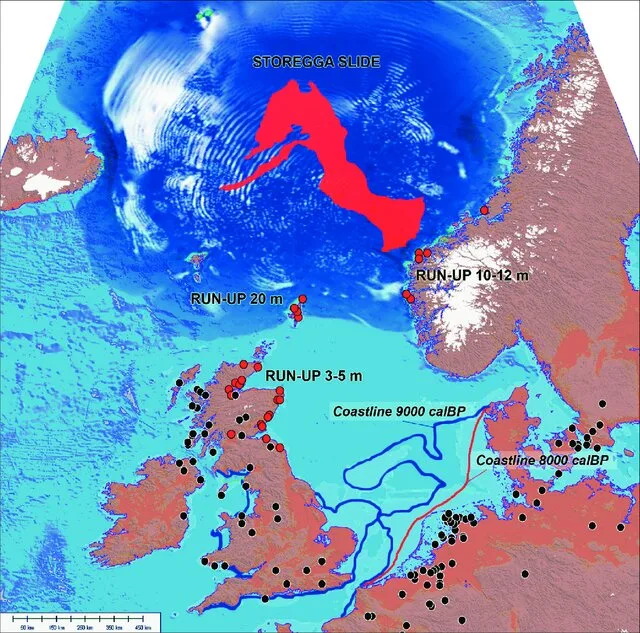
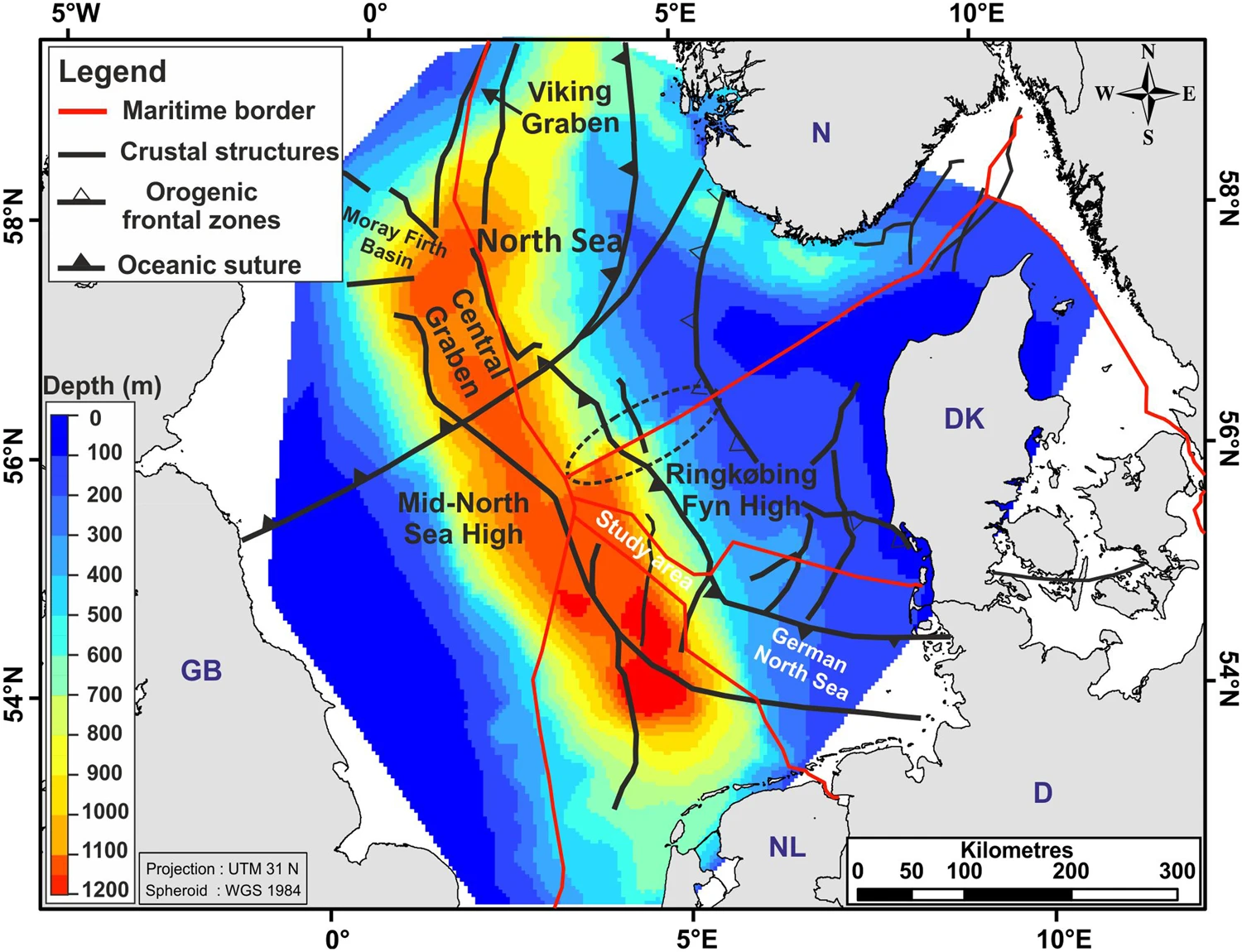
DOI https://doi.org/10.4312/dp.35.1 Abstract Around 8200 calBP, large parts of the now submerged North Sea continental shelf (‘Doggerland’) were catastrophically flooded by the Storegga Slide tsunami, one of the largest tsunamis known for the Holocene, which was generated on the Norwegian coastal margin by a submarine landslide. In the present paper, we derive a precise calendric date for the Storegga Slide tsunami, use this date for reconstruction of contemporary coastlines in the North Sea in relation to rapidly rising sea-levels, and discuss the potential effects of the tsunami on the contemporaneous Mesolithic population. One main result of this study is an unexpectedly high tsunami impact assigned to the western regions of Jutland. Weninger, B., Schulting, R., Bradtmöller, M., Clare, L., Collard, M., Edinborough, K., Hilpert, J., Jöris, O., Niekus, M., Rohling, E. J., & Wagner, B. (2008). The catastrophic final flooding of Doggerland by the Storegga Slide tsunami. Documenta Praehistorica, 35, 1-24. https://doi.org/10.4312/dp.35.1