DOI https://doi.org/10.1144/sp469.24
Abstract
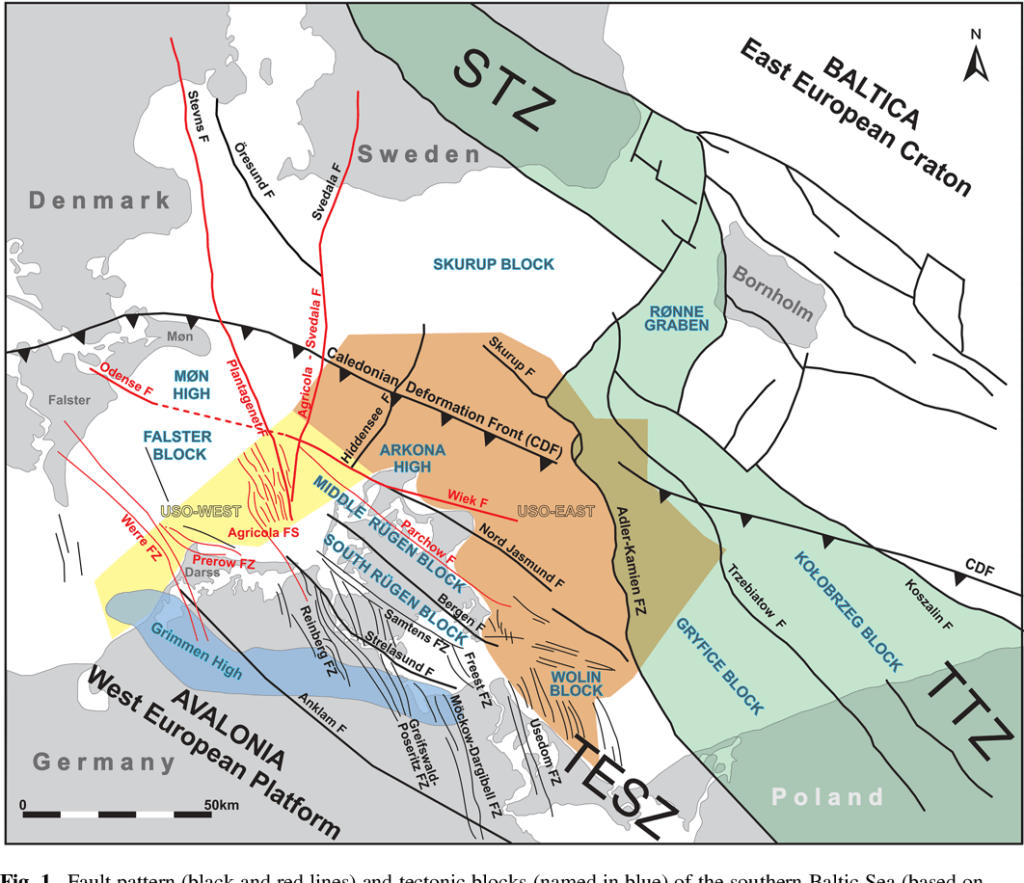
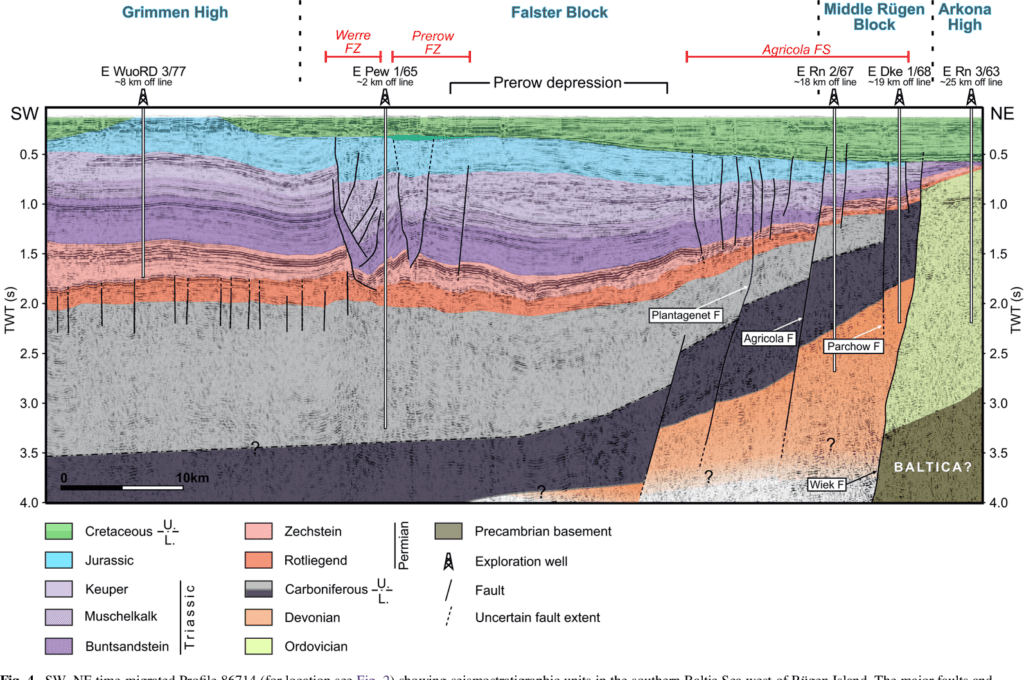
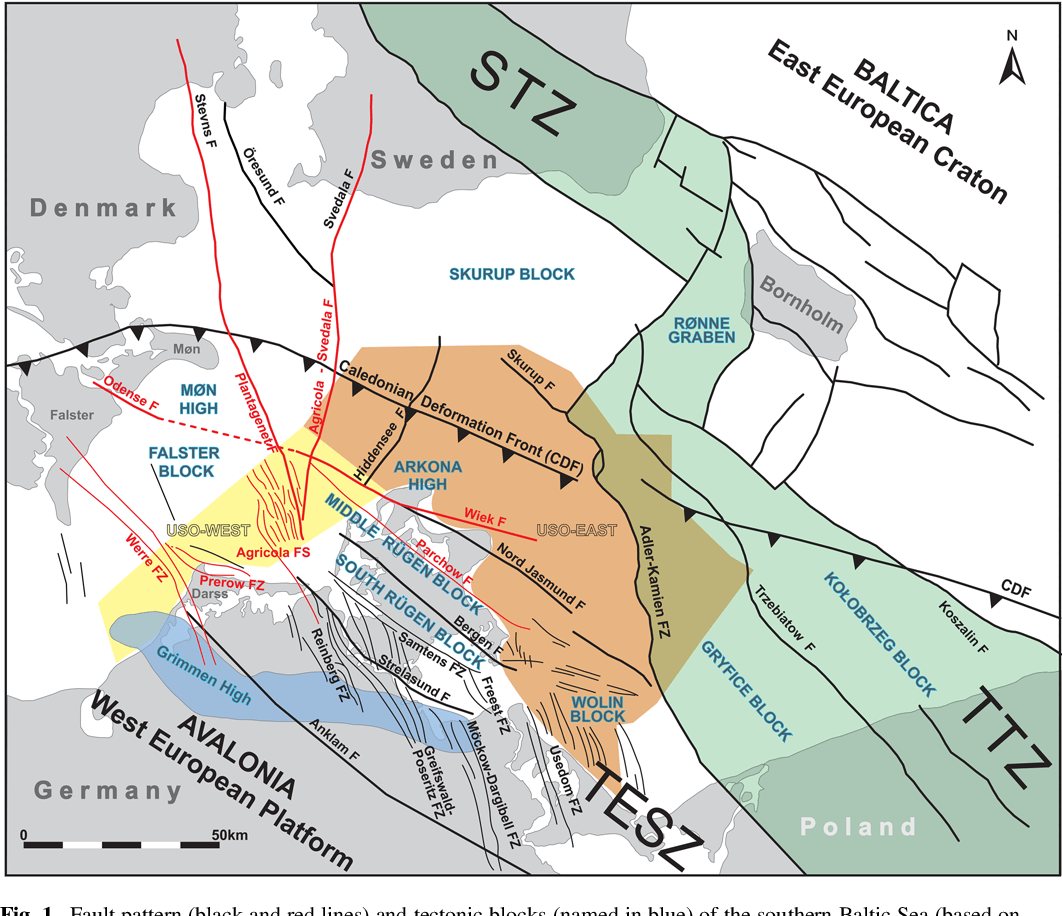
Based on reprocessed offshore seismic lines acquired during oil and gas exploration in the 1980s, we reconstruct the formation and reactivation of major fault systems in the southern Baltic Sea area since the late Paleozoic. The geological evolution of different crustal blocks from the Caledonian Avalonia-Baltica collision until the Late Cretaceous-Paleogene inversion tectonics is also examined. The detected fault systems occur in the northern part of the Trans-European Suture Zone (TESZ) and belong either to the late Paleozoic Tornquist Fan or to the complex Western Pomeranian Fault System (WPFS) generated during Mesozoic extensional movements. While the NW- SE-trending deep Wiek Fault separates the Arkona High from the Middle Rügen Block, the NNW-SSE-trending Agricola Fault demarcates the Middle Rügen Block to the Falster Block in the west. Together with the Plantagenet Fault and numerous younger faults in the Mesozoic cover, it forms the Agricola Fault System. Furthermore, structural analyses of the Prerow Fault Zone above the Prerow salt pillow and the Werre Fault Zone crossing the Grimmen High indicate a complex fault history.
Deutschmann, Andre & Meschede, Martin & Obst, Karsten. (2018). Fault system evolution in the Baltic Sea area west of Rügen, NE Germany. Geological Society, London, Special Publications. 469. SP469.24. 10.1144/SP469.24.